What Are Joint Travel Regulations?
GSA Schedule | 5 Min Read
When it comes to traveling, whether it’s for a vacation, visiting family, or for work, expenses can pile up. Luckily, for GSA Schedule contract holders, several costs associated with traveling under your contract are covered by Joint Travel Regulations (JTRs). Joint Travel Regulations establish travel and transportation allowances. Depending on the agency you are performing the work under, JTRs could also be referred to as Federal Travel Regulations (FTRs), which are similar in nature. Here’s what you need to know about Joint Travel Regulations and when they apply to you.
What Are Joint Travel Regulations?
Joint Travel Regulations implement policies and laws establishing travel and transportation allowances for individuals traveling for official business under a government contract. Agencies typically issue charge cards to contractors which are used to pay for official travel and transportation related expenses.
Through JTRs, agencies may pay for expenses that are necessary for contractors (including GSA schedule contract holders) to execute their work under their government contract. Costs covered includes:
- Transportation expenses
- Per diem expenses
- Miscellaneous expenses
- Travel expenses
Transportation expenses are defined as fares, rentals, mileage payments, and other costs related to transportation. In the Federal Travel Regulations document, miscellaneous fees are cost such as conversion of foreign currency, passport/visa, foreign country exit fee, and inoculations. Miscellaneous may be covered if authorized and approved by a government agency prior to incurring expenses. However, damage or loss of clothing, luggage, and personal artifacts are listed among expenses that will not be covered. Travel cost and expenses are covered via per diem rates or line-item rates, which we’ll cover below.
What happens if you have expenses that do not line up with one of the costs covered above? Travelers will be subject to pay any cost not in compliance with JTRs, so to avoid out of pocket expense, it’s important to understand what exactly is covered for travel under your GSA contract.
How are Joint Travel Regulations Managed?
Per Diem Rates
Per Diem rates are the allowances for lodging (not including taxes), meals, and incidental expenses. Examples of incidental expenses are costs associated with tipping or baggage handling. It’s important to note that the rates allotted for meals and incidentals are slightly reduced for the first and last day of travel. Within the lower Continental United States (CONUS), the rates Per Diem are established by GSA. The standard Per Diem rate allocated by most of CONUS is $155 ($96 for lodging, $59 for meals and incidental expenses).
Foreign rates are established by the State Department and non-foreign rates which include Alaska, Hawaii, and U.S. territories are established by the Department of Defense (DoD). GSA establishes rates Per Diem cost at the beginning of each fiscal year by location on October 1st. To find the cost Per Diem for your contract site, visit gsa.gov.
Per Diem lodging is determined by hotels rates for one room per night in each locality. These rates may change depending on the season. An example of Per Diem rates for certain cities in Virginia can be seen below:
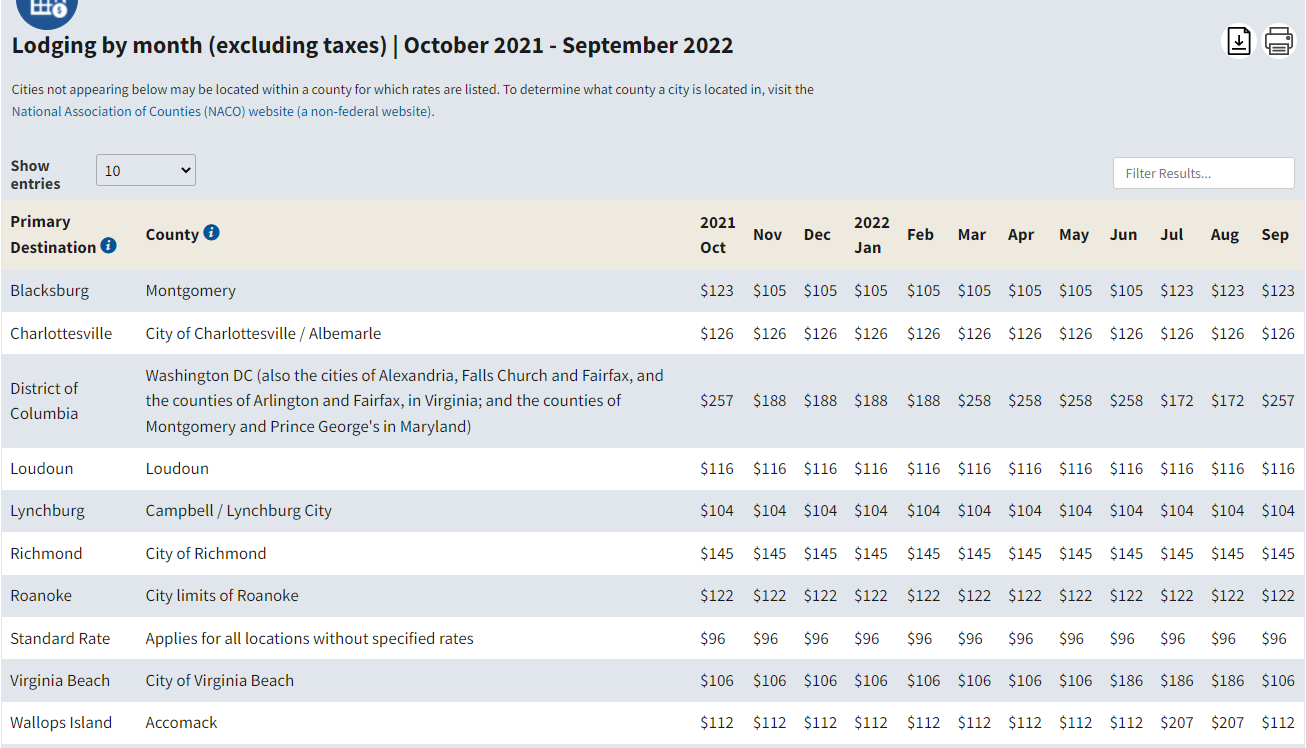
How do you find the Per Diem rate for your contract location? You can go to GSA’s webpage on Per Diem rates, and just enter the city or state of the contract location and view the lodging rates by month excluding taxes. It shows the rates for the entire fiscal year which is from October 1 to September 30. The same information can be found for meals and incidentals if you toggle over to the “M&IE” button, or scroll down on the same page:
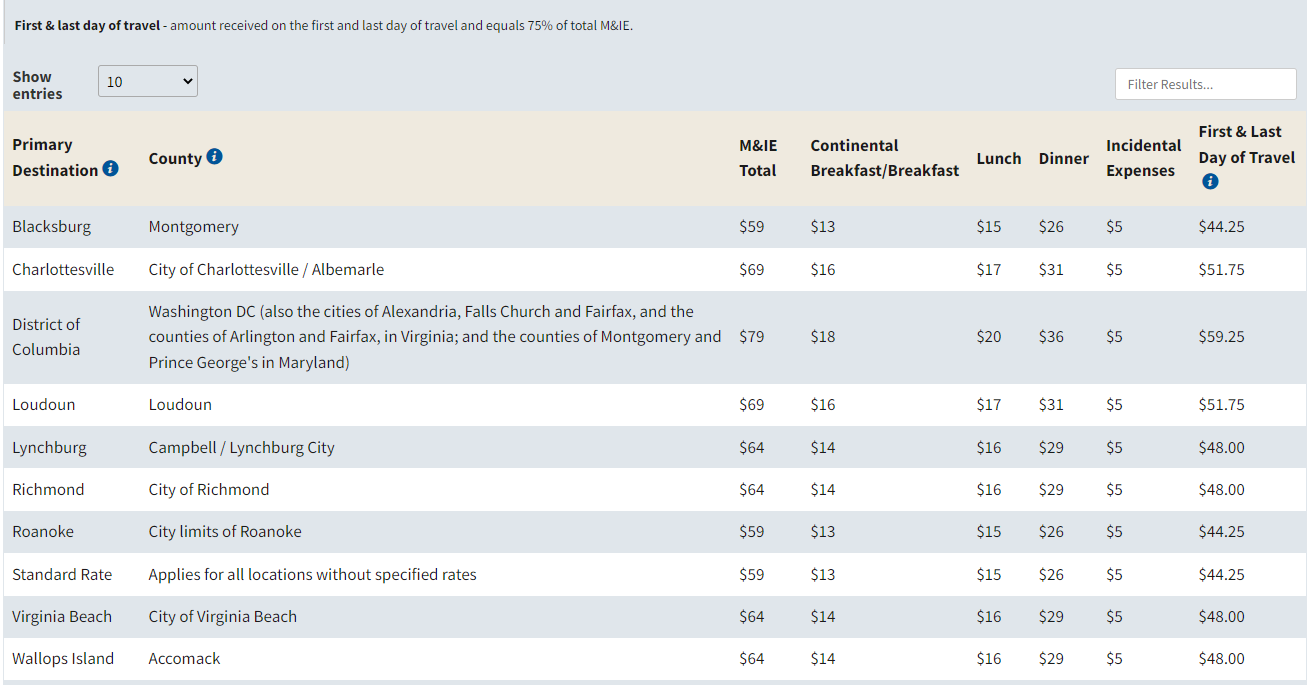
Per Diem allowances are separate from transportation expenses. However, vendors can receive Per Diem rates for hotels, car rentals, and flight costs which are tax exempt after presenting your Common Access Card (CAC). CACs are provided to all employees traveling for federal work. When Per Diem rates are not adequate to cover travel cost and expenses (meal and incidentals), JTRs allow for actual expense reimbursement.
Line-Item Rates
Line-Item rates are another way in which travel costs are covered. Cost of travel can be listed on your task order as a Cost Line-Item Number (CLIN). CLINs list line by line every cost aspect of a project and are determined by your Contracting Officer Representative (COR). When invoicing the CLIN for travel on a task order, the actual expense cannot exceed the allotted funds specified while traveling. Even if there are administrative or time costs for booking travel, there can be absolutely no mark-ups. If funds exceed established amount, your company is liable to cover the difference. These travel expenses can also be tax exempt just like with Per Diem rates.
When is Cost of Travel Covered for Your GSA Contract?
To recap, cost of travel through your GSA Schedule is covered by Federal Travel Regulations (FTRs) or Joint Travel Regulations (JTRs) depending on the agency you work with. As mentioned above, fares, rental fees, mileage payments, and any other costs associated with traveling to and from the place of performance are covered.
When is Cost of Travel Not Covered?
If there is a cost that lies outside of the pre-set price for either Per Diem rates or CLIN (Cost Line-Item number), then it is not covered. Additionally, any travel cost that is not explicitly allowed by the government agency, or any non-advantageous travel outside of the limits set by the government agency. For example, if you happen to be performing work on your contract in Los Angeles, a trip to San Diego or Palm Springs to check out the area will be your responsibility.
Expectations for GSA Contractors Post-Award
It’s important for GSA contractors to know how to comply with Joint Travel Regulations. When invoicing government agencies, lodging and airline receipts must be provided. However, receipts for meals and incidentals are not required when invoicing. This ensures proper compensation for travel. You’ll want to submit the required information to GSA no later than 60 days after the end of each fiscal year.
Additionally, all travel expenses are tax exempt. The tax exemption form can be found on GSA’s site. Keep in mind that the cost of travel for any GSA order should NOT be reported in quarterly/monthly sales and the Industrial Funding Fee (IFF) should not be paid on travel cost related to GSA projects.
Do You Have Questions About Properly Managing Your GSA Schedule?
If you have questions about managing your GSA Schedule whether it’s for Joint Travel Regulations, properly invoicing and reporting your sales, or just general questions about your contract, we would be happy to help you. If you want to learn more in depth about Joint Travel Regulations, we have a webinar on-demand you can download and watch on your own time.